|
查看: 2414|回复: 13
|
有关RELAY的问题
[复制链接]
|
|
|
想请问有关RELAY的功能与应用。
据我所知, RELAY 多数可以在以下的产品找到
1。家庭 WATER HEATER
2。家庭电动门 AUTO GATE
3。电能输送转换站
4。其他
谢谢各位的帮忙。 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 发表于 14-8-2009 06:26 PM
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 14-8-2009 06:26 PM
|
显示全部楼层
原帖由 魔术 于 14-8-2009 05:40 PM 发表 
想请问有关RELAY的功能与应用。
据我所知, RELAY 多数可以在以下的产品找到
1。家庭 WATER HEATER
2。家庭电动门 AUTO GATE
3。电能输送转换站
4。其他
谢谢各位的帮忙。
Relay,中文叫做“继电器”
分为:Coil 和 Contact 两大部分!~
主要用途是用小量电流来达成较大电流的电动开关器!~
Coil即是线圈,扮演着电磁铁的角色,
Contact即是触点,分为Com,NC,NO
NC=Normally Closed,
NO=Normally Open,
Com=公用触点( ??不会解释,随人帮忙下)
当没有电流通过Coil时,NC和Com是可通电的,NO和Com是不可通电的,
当电流通过Coil时,Coil所产生磁力会把连接着NC和Com的一片铁片转向连接NO和Com,
形成NC和Com是不通电的,NO和Com是通电的!~ |
评分
-
查看全部评分
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 发表于 14-8-2009 06:57 PM
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 14-8-2009 06:57 PM
|
显示全部楼层
希望你看得明白!~
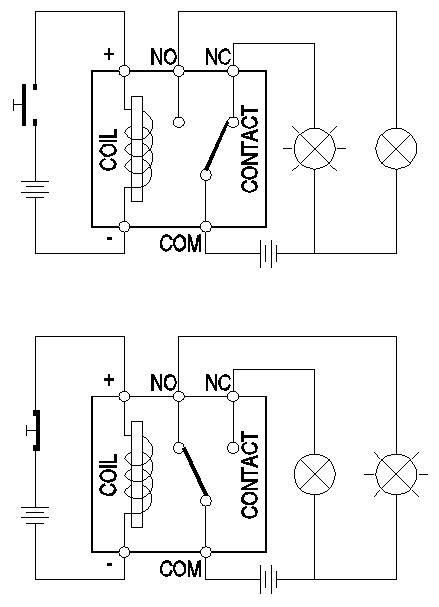 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 发表于 14-8-2009 08:15 PM
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 14-8-2009 08:15 PM
|
显示全部楼层
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 发表于 14-8-2009 09:09 PM
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 14-8-2009 09:09 PM
|
显示全部楼层
Relay/Contactor:
种类:
1. 体积/形状/重量(看#4)
2. 接脚,如:方形的8pin, 14pin, 圆形的8pin, 11pin
3. 操作,如:Latch Relay
4. 用途等等。。。
Coil的电压:
驱动Relay开关所需电压,常用:
AC24, AC230, AC415
DC12, DC24
Coil的电耗:
驱动Relay开关所需的耗电量,不会很大,小小而已!~
Poles:
一粒Relay/Contactor里拥有的整套Contact/接点数量,如:
1NC/1NO和1COM = 1 Pole
2NC/2NO和2COM = 2 Poles
通常最高4Poles!~
Contact/接点:
1. 接点通过最大电流的能力。。。
2. 接点使用金属原料(铜,金,银,白金等等)
3. 接点电阻
4. 启动开/关的时间(很快,ms计算)
寿命:
开/关次数计算
工作环境:
1. 温度
2. 湿度
IEC 947-4标准规格:
AC-1 This applies to all AC loads where the power factor is at least 0.95.
These are primarily non-inductive or slightly inductive loads. Breaking remains easy.
AC-2 This applies to Slip-ring motors; starting, switching off.
AC-3 This applies to squirrel cage motors where the breaking of the power contacts would occur while the motor is running.
On closing, the contactor experiences an inrush which is 5-8 times the nominal current, and at this instant,
the voltage at the terminals is approximately 20% or the line voltage. Breaking remains easy.
AC-4 This applies to the starting and breaking of a squirrel cage motor during an inch or plug reverse operation.
On energization, the contactor closes on an inrush current approx. 5-8 times the nominal current of the motor.
On de-energization, the contactor breaks the same magnitude of nominal current at a voltage that can be equal to the supply voltage.
Breaking is severe.
AC-5a Switching of electric discharge lamps
AC-5b Switching of incandescent lamps
AC-6a Switching of transformers
AC-6b Switching of capacitor banks
AC-7a Slightly inductive loads in household appliances and similar applications
AC-7b Motor-loads for household applications
AC-8a Hermetic refrigerant compressor-motor control w/ manual resetting of overload releases
AC-8b Hermetic refrigerant compressor-motor control w/ automatic resetting of overload releases
DC-1 This applies to all DC loads where the time constant (L/R) is less than or equal to one msec.
These are primarily non-inductive or slightly inductive loads.
DC-3 This applies to starting and breaking of a shunt motor during inching or plugging.
The time constant shall be less than or equal to 2 msec. On energization, the contactor sees current similar to that in Cat. DC-2.
On de-energization, the contactor will break around 2.5 times the starting current at a voltage that may be higher than the line voltage.
This would occur when the speed of the motor is low because the back e.m.f. is low. Breaking is severe.
DC-5 This applies to the starting and breaking of a series motor during inching or plugging. The time constant being less that or equal to 7.5 msec.
On energization, the contactor sees about 2.5 times the nominal full load current.
On de-energization, the contactor breaks the same amount of current at a voltage which can be equal to the line voltage. Breaking is severe.
DC-6 Switching or incandescent lamps
转自:http://www.sescowi.com/Default.aspx?tabid=195
这都是标准规格,懒惰翻译,请原谅!~ 
其他:
如有遗漏或误导,期待其他网友的补充和指点了。。。 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 发表于 14-8-2009 09:17 PM
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 14-8-2009 09:17 PM
|
显示全部楼层
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 发表于 14-8-2009 09:19 PM
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 14-8-2009 09:19 PM
|
显示全部楼层
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

楼主 |
发表于 15-8-2009 09:07 AM
|
显示全部楼层
真的谢谢大家的帮忙。
楼上的朋友太厉害了。
请问有那些产品可以找到RELAY呢 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 发表于 15-8-2009 11:44 AM
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 15-8-2009 11:44 AM
|
显示全部楼层
com 是stand for common...就是不管是no @ nc... common都是得接的...
打开车的引擎盖...应该有个relay box吧... 我没什么研究车...但好像有看过... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 发表于 15-8-2009 01:17 PM
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 15-8-2009 01:17 PM
|
显示全部楼层
|
还有SSR= SOLID STATE RELAY, 没有coil的。比较贵 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 发表于 15-8-2009 10:59 PM
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 15-8-2009 10:59 PM
|
显示全部楼层
原帖由 PirateOfLove 于 15/8/2009 13:17 发表 
还有SSR= SOLID STATE RELAY, 没有coil的。比较贵
SOLID STATE RELAY是不是有一種可以 4-20mA CONTROL INPUT/ MODULATING 巴仙 POWER OUTPUT的??? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 发表于 17-8-2009 09:51 AM
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 17-8-2009 09:51 AM
|
显示全部楼层
原帖由 PirateOfLove 于 15-8-2009 01:17 PM 发表 
还有SSR= SOLID STATE RELAY, 没有coil的。比较贵
没看过玩过研究过。。。
不如大大你来分享下!~  |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 发表于 24-9-2009 01:39 PM
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 24-9-2009 01:39 PM
|
显示全部楼层
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 发表于 24-9-2009 01:43 PM
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 24-9-2009 01:43 PM
|
显示全部楼层
原帖由 tiast 于 15-8-2009 10:59 PM 发表 
SOLID STATE RELAY是不是有一種可以 4-20mA CONTROL INPUT/ MODULATING 巴仙 POWER OUTPUT的???
不是 啦。 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
 本周最热论坛帖子 本周最热论坛帖子
|